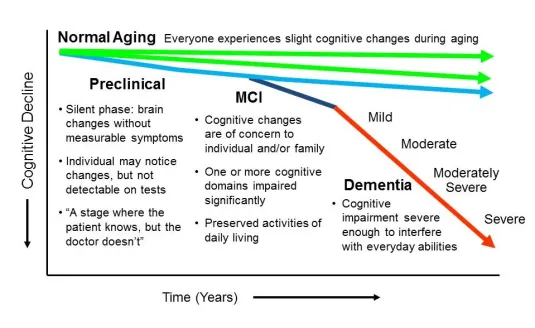
Introduction: Understanding Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) and Its Assessment
Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is a condition that affects cognitive functions such as memory, language, and decision-making. It is often considered a transitional stage between normal aging and dementia. Assessing MCI properly is crucial for early detection and intervention to prevent further cognitive decline. In this blog, we will explore the different assessment methods for MCI, the importance of early detection, and how healthcare professionals can better support patients with this condition.

2. The Importance of Early Detection in Mild Cognitive Impairment
Early detection of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is paramount in effectively managing and potentially slowing down cognitive decline. Identifying MCI in its early stages allows for prompt intervention and implementation of strategies to enhance cognitive function and quality of life. Additionally, early detection enables healthcare professionals to provide patients and their families with appropriate support, education, and resources for coping with the challenges associated with MCI. Stay tuned as we delve deeper into the significance of early detection in MCI and discuss practical steps for individuals and caregivers to take in response to an MCI diagnosis.
3. Overview of Assessment Tools and Techniques for MCI
3. Overview of Assessment Tools and Techniques for MCI
Assessing mild cognitive impairment often involves a comprehensive evaluation utilizing various tools and techniques to measure cognitive function, memory, language skills, and other areas affected by MCI. Health professionals may use standardized tests, questionnaires, and cognitive assessments to assess the severity and progression of the condition. These assessments help in determining the level of impairment, tracking changes over time, and informing personalized treatment plans. In the upcoming sections, we will explore common assessment tools used in diagnosing MCI and discuss how these evaluations aid in the management and care of individuals living with this condition. Stay informed for valuable insights on navigating the assessment process effectively.
4. Key Criteria for Diagnosing Mild Cognitive Impairment
4. Key Criteria for Diagnosing Mild Cognitive Impairment
Diagnosing mild cognitive impairment (MCI) requires careful consideration of specific criteria to differentiate it from normal aging or dementia. Key criteria commonly used include evidence of cognitive decline beyond what is expected for age, preserved independence in functional activities, absence of significant impairment in daily living, and not meeting criteria for dementia. Understanding these criteria is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate intervention planning. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into each criterion, providing insights on how they contribute to identifying and managing MCI effectively. Stay tuned for expert guidance on navigating the diagnostic process with confidence and clarity.
5. Best Practices for Conducting Comprehensive MCI Assessments
5. Best Practices for Conducting Comprehensive MCI Assessments
Conducting a thorough assessment for mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is essential for accurate diagnosis and individualized treatment planning. Best practices include utilizing a combination of cognitive tests, clinical interviews, medical history reviews, and input from family members or caregivers. Collaborating with a multidisciplinary team, including neuropsychologists, neurologists, and geriatricians, enhances assessment accuracy and ensures a holistic approach to care. In the upcoming sections, we will discuss the importance of each assessment component, common tools used for evaluation, and strategies for interpreting assessment results. Stay informed on how to conduct comprehensive MCI assessments effectively to support patients and their families in managing cognitive changes with compassion and expertise.
6. Challenges in MCI Assessment and Strategies for Effective Solutions
6. Challenges in MCI Assessment and Strategies for Effective Solutions
Despite best practices, challenges may arise during MCI assessments. Some common obstacles include variations in symptom presentation, patient reluctance to disclose impairments, and competing medical conditions influencing cognitive performance. To address these challenges, it is crucial to establish a trusting and supportive relationship with the patient, encourage open communication, and tailor assessments to individual needs. Implementing standardized assessment protocols, frequent reassessments, and ongoing education for healthcare professionals can enhance the accuracy of MCI evaluations. In the following sections, we will delve into specific strategies to overcome these challenges and optimize the assessment process for improved patient outcomes. Stay tuned for valuable insights on navigating complexities in MCI assessment.
7. Conclusion: Advancing MCI Assessment for Better Patient Outcomes
In conclusion, recognizing and addressing the challenges in Mild-Cognitive Impairment (MCI) assessments is fundamental to improving patient outcomes and quality of care. By understanding the nuances of MCI symptomatology and patient interactions, healthcare professionals can implement targeted strategies to enhance assessment accuracy and effectiveness. From fostering trust and open communication with patients to utilizing standardized protocols and continuous education, a comprehensive approach can elevate MCI evaluations. As we continue to explore innovative solutions and best practices in MCI assessment, let us prioritize the well-being and cognitive health of individuals facing these challenges. Together, we can advance MCI assessment practices for the benefit of patients and healthcare providers alike.